by Angela
Share

When working with RF systems, two key performance indicators often come up—VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) and Return Loss. Though closely related, these two terms describe signal reflections in different ways. Understanding both is essential for evaluating signal integrity and optimizing RF transmission lines.
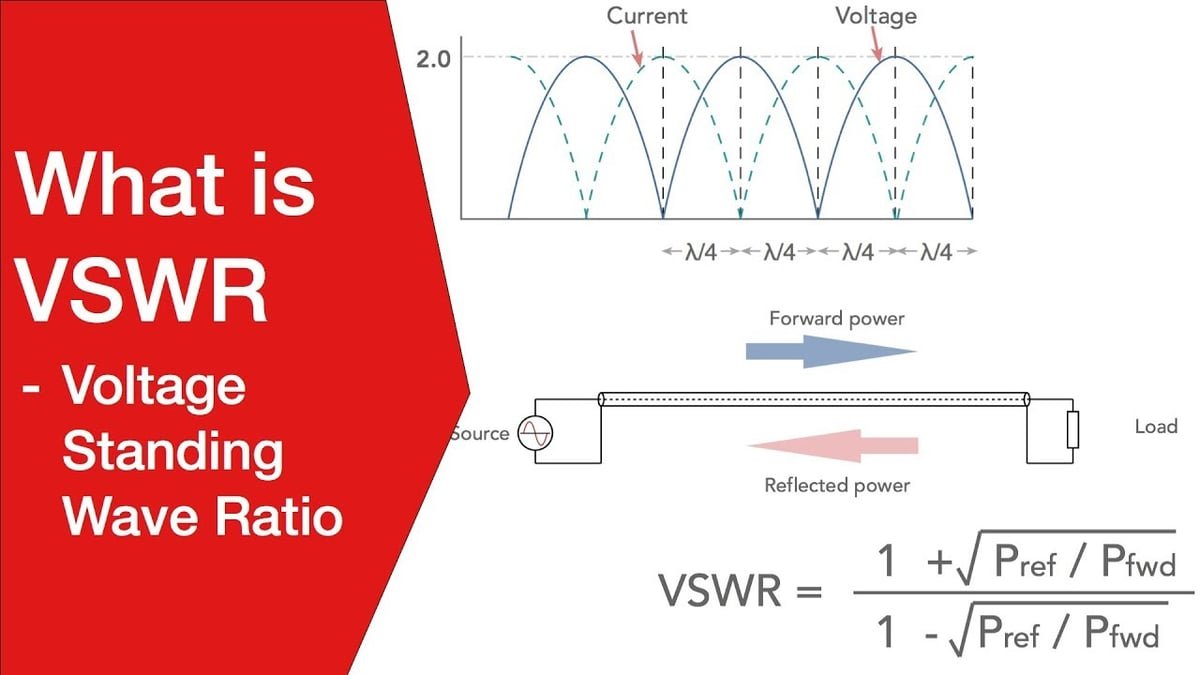
📈 What Is VSWR?
VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) is a measure of how efficiently RF power is transmitted from a source to a load through a transmission line. It represents the ratio between the maximum and minimum voltages in a standing wave pattern along the line.
-
Ideal VSWR: 1:1 (perfect match, no reflection)
-
Typical Range: 1.0 (best) to ∞ (worst)
-
A high VSWR means more signal is being reflected back, which can lead to signal loss, heating, or equipment damage.
📉 What Is Return Loss?
Return Loss quantifies the amount of power that is reflected back toward the source, expressed in decibels (dB). It is calculated as the ratio of reflected power to incident power, on a logarithmic scale.
-
Higher Return Loss = Better Performance
-
For example, 20 dB return loss means only 1% of the power is reflected.
-
It’s a positive value, and the higher the number, the lower the reflection.
🔄 VSWR vs. Return Loss: Key Differences
Here’s a simplified comparison:
| Parameter | VSWR | Return Loss |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voltage ratio (Vmax/Vmin) | Reflected vs. incident power |
| Unit | Unitless ratio (e.g., 1.5:1) | Decibels (dB) |
| Ideal Value | 1:1 | ∞ dB |
| Reflection Quality | Low VSWR = better match | High RL = better match |
| Interpretation | Harder to measure directly | Easier with modern tools |
🔧 Which One Should You Use?
-
Return Loss is often preferred in design and testing because it directly represents signal quality and is easier to read using network analyzers.
-
VSWR is more common in specifications for antennas and connectors.
📌 Conclusion
Both VSWR and Return Loss provide insights into how well an RF system is performing. A good understanding of both helps engineers optimize their designs for low signal loss, minimal reflection, and high efficiency.
Need precision RF components designed for optimal VSWR and Return Loss? Visit Reach-line for high-performance RF connectors, cables, and test solutions.
STAY IN FOR MORE NEWS
Subscribe to our free newsletter.
RF, microwave, and millimeter-wave describe frequency ranges with distinct uses. RF covers 3 kHz to 300 GHz, including microwaves and mmWave. Microwaves occupy 300 MHz to 300 GHz, while mmWave strictly focuses on 30 GHz to 300 GHz. Each handles specific tech needs.
Introduction to VSWR Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) is a critical parameter in RF (Radio Frequency) systems, indicating how effectively power is transferred from a source to a load. It measures the ratio of the maximum to the minimum voltage in a standing wave formed by reflected and transmitted signals.
The evolution of 5G technology has brought immense benefits—but also unprecedented challenges—particularly in the field of RF testing and measurement. As new technologies like millimeter wave, beamforming, and ultra-wideband become essential to 5G, traditional testing methods are no longer sufficient. Over-the-air (OTA) testing is now central to ensuring performance and compliance with 5G NR standards.
Discover Reach-Line’s precision RF and microwave terminations covering DC to 110 GHz and power levels 1 W to 1000 W. Reliable, low VSWR solutions for 5G, satellite, and lab applications.