by Angela
Share

The evolution of 5G technology has brought immense benefits—but also unprecedented challenges—particularly in the field of RF testing and measurement. As new technologies like millimeter wave, beamforming, and ultra-wideband become essential to 5G, traditional testing methods are no longer sufficient. Over-the-air (OTA) testing is now central to ensuring performance and compliance with 5G NR standards.
📡 The Shift to OTA Testing
Unlike in previous generations where testing was done via coaxial cable connections in RF labs, 5G devices often lack physical connectors. As a result, OTA testing has become the dominant method. In OTA testing, measurement tools communicate wirelessly with the device under test, simulating real-world scenarios and capturing crucial performance data.
This shift affects not only antenna validation but also the entire RF system, requiring engineers to test complete devices and systems in situ.
⚙️ Technical Complexity in the 5G Landscape
From a technical standpoint, 5G represents a significant leap in spectrum efficiency—5 to 15 times higher than 4G—and introduces high data rates in the gigabit-per-second range. Supporting this performance requires advanced technologies such as:
-
Millimeter Waves
-
Phased Array Beamforming
-
Massive MIMO
-
Ultra-Wideband Communications
These innovations introduce intricate design considerations and require advanced testing protocols aligned with 5G NR specifications.
🧪 A New Testing Paradigm
Testing in the 5G era is not just about verifying signal quality—it’s about validating beam tracking, steering agility, and ensuring adaptive antenna systems perform as expected across countless use-case scenarios.
For example, unlike static antennas used in 3G/4G systems, 5G’s steerable beam antennas dynamically direct energy toward the user device. These beams, generated by phased array antennas, must be precisely calibrated through OTA testing across many operational angles and configurations.
🔍 Conclusion: The Industry’s Growing Demand for OTA Solutions
As Mathieu Mercier notes, “The test environment in the 5G era has undergone a dramatic shift, and OTA methods have become the new mainstream.” The increasing reliance on wireless device performance in real-world conditions demands OTA testing solutions that are agile, accurate, and scalable.
To succeed in this era, test and measurement professionals must embrace OTA testing not just as a technique, but as a fundamental pillar of 5G device validation and system optimization.
STAY IN FOR MORE NEWS
Subscribe to our free newsletter.
RF, microwave, and millimeter-wave describe frequency ranges with distinct uses. RF covers 3 kHz to 300 GHz, including microwaves and mmWave. Microwaves occupy 300 MHz to 300 GHz, while mmWave strictly focuses on 30 GHz to 300 GHz. Each handles specific tech needs.
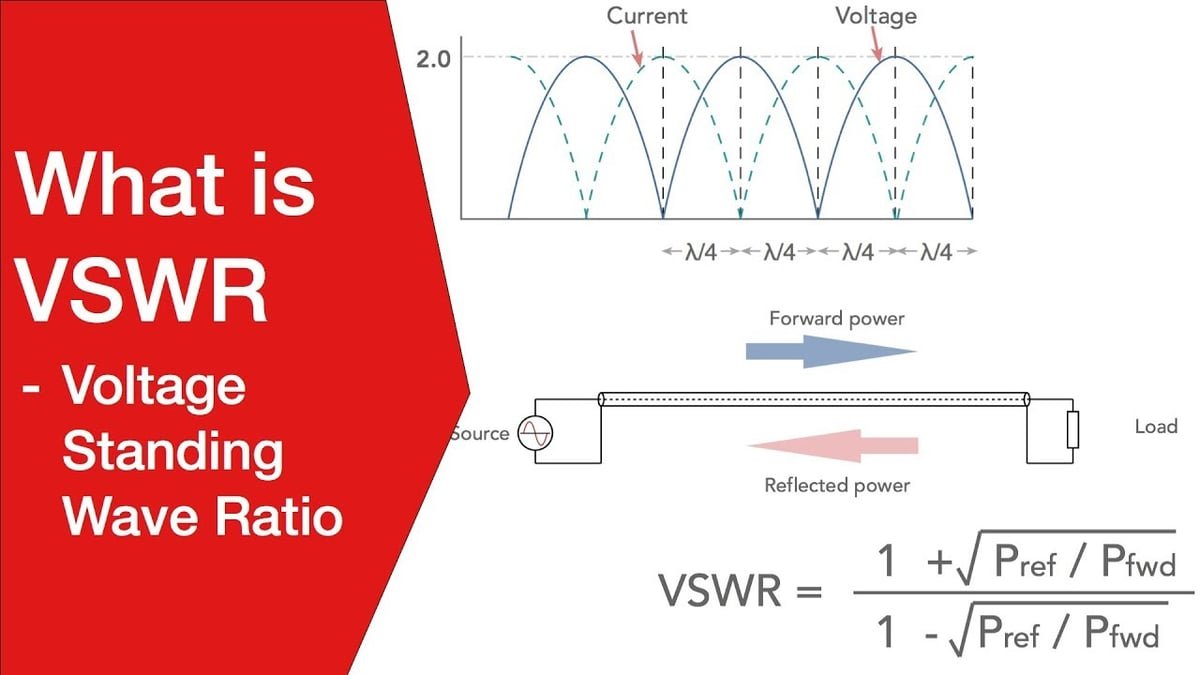
Introduction to VSWR Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) is a critical parameter in RF (Radio Frequency) systems, indicating how effectively power is transferred from a source to a load. It measures the ratio of the maximum to the minimum voltage in a standing wave formed by reflected and transmitted signals.
Discover Reach-Line’s precision RF and microwave terminations covering DC to 110 GHz and power levels 1 W to 1000 W. Reliable, low VSWR solutions for 5G, satellite, and lab applications.
Reach-Line offers high-frequency cable assemblies, fixed attenuators, and precision terminations. Partner for engineering support, rapid prototyping, and global logistics.