by Angela
Share

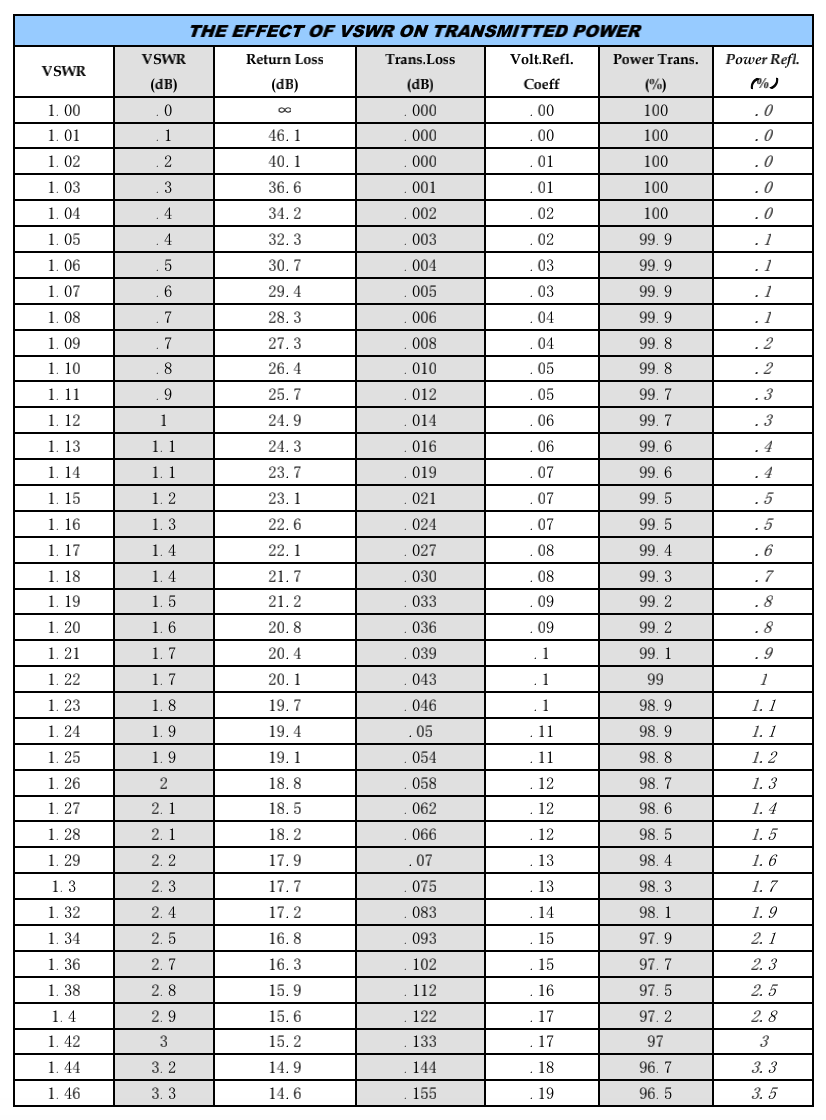
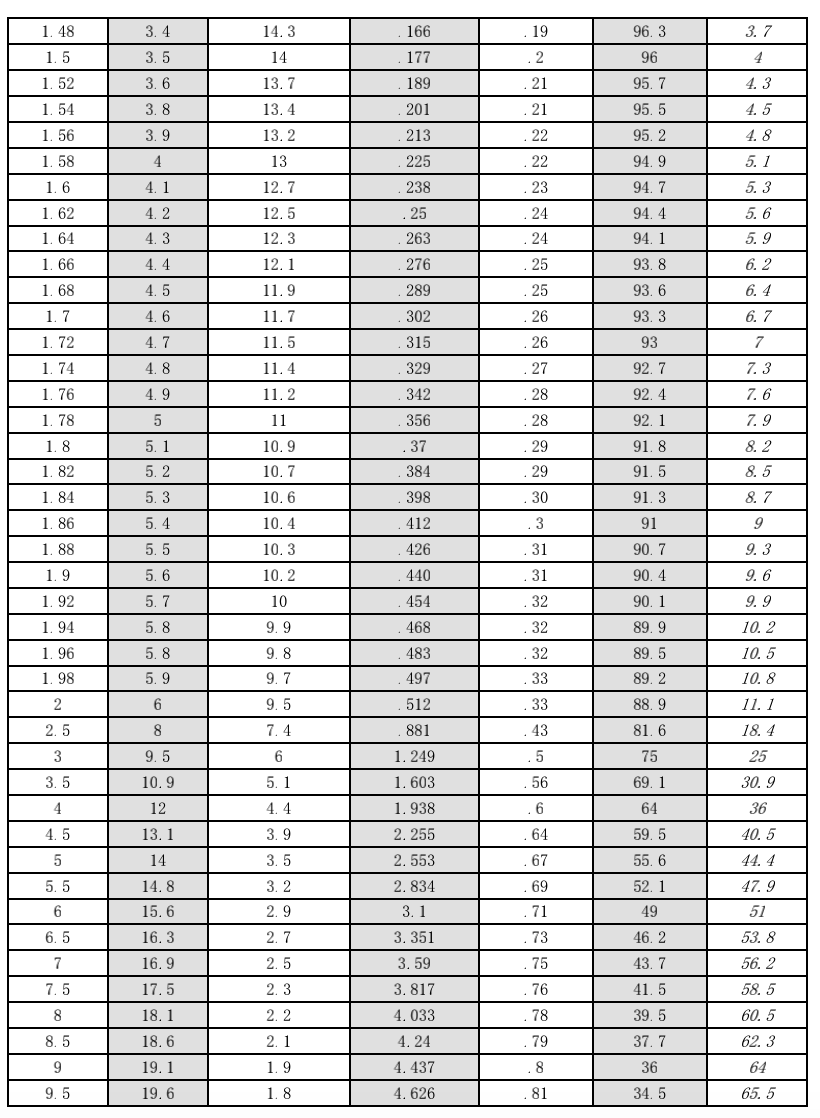
If you are a newcomer in the RF industry, it must be difficult to distinguish VSWR and return loss. The following is a comparison table of VSWR and return loss.
-
What is VSWR
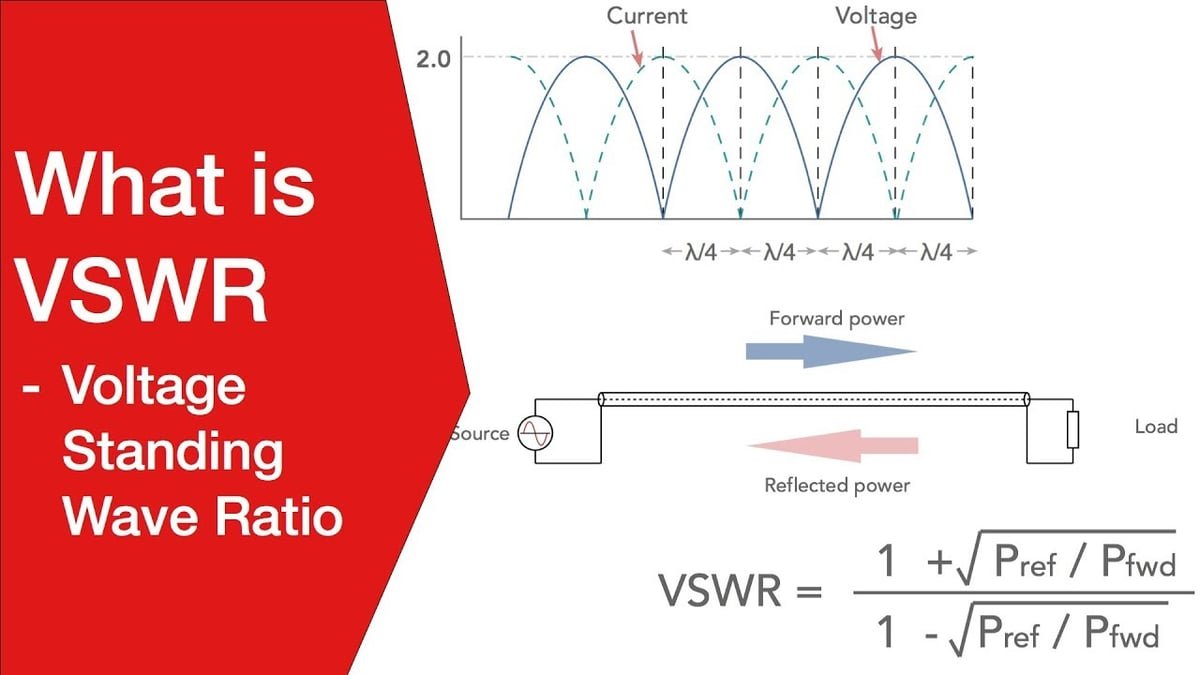
VSWR ( (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio)is defined as the ratio of the maximum voltage to the minimum voltage in standing wave pattern along the length of a transmission line structure. It varies from 1 to (plus) infinity and is always positive. Unless you have a piece of slotted line-test equipment this is a hard definition to use, especially since the concept of voltage in a microwave structure has many interpretations.
-
What is Return loss (RL)
Return loss (RL) is the ratio of the reflected power to the incident power, in decibels (dB).
-
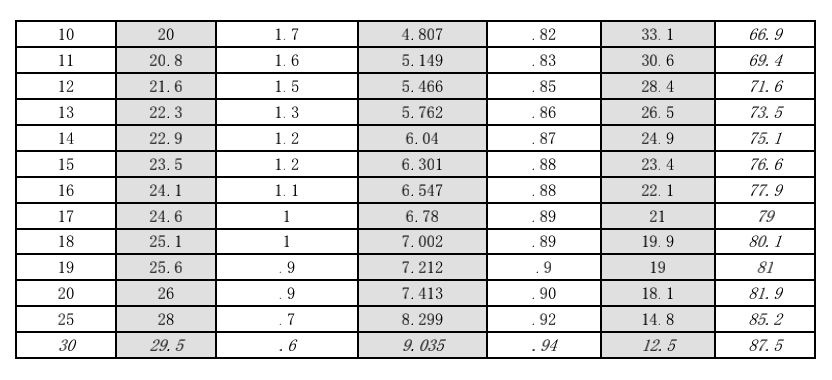
The Comparison table of VSWR and Return Loss
STAY IN FOR MORE NEWS
Subscribe to our free newsletter.
RF, microwave, and millimeter-wave describe frequency ranges with distinct uses. RF covers 3 kHz to 300 GHz, including microwaves and mmWave. Microwaves occupy 300 MHz to 300 GHz, while mmWave strictly focuses on 30 GHz to 300 GHz. Each handles specific tech needs.
Introduction to VSWR Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) is a critical parameter in RF (Radio Frequency) systems, indicating how effectively power is transferred from a source to a load. It measures the ratio of the maximum to the minimum voltage in a standing wave formed by reflected and transmitted signals.
The evolution of 5G technology has brought immense benefits—but also unprecedented challenges—particularly in the field of RF testing and measurement. As new technologies like millimeter wave, beamforming, and ultra-wideband become essential to 5G, traditional testing methods are no longer sufficient. Over-the-air (OTA) testing is now central to ensuring performance and compliance with 5G NR standards.
Discover Reach-Line’s precision RF and microwave terminations covering DC to 110 GHz and power levels 1 W to 1000 W. Reliable, low VSWR solutions for 5G, satellite, and lab applications.