by Angela
Share

Radar systems are essential to modern detection and ranging technologies, widely used in aerospace, defense, automotive, weather monitoring, and beyond. But what exactly is radar, and how do radar frequency bands work? Let’s dive in.
🧭 What Is Radar?
RADAR stands for Radio Detection And Ranging. It works by transmitting electromagnetic waves through space and analyzing the echoes that bounce back from distant objects. This process enables radar systems to detect the presence, position, velocity, and size of targets such as aircraft, ships, or terrain features.
📡 What Are Radar Bands?
Radar bands define the specific frequency ranges at which radar systems operate. These frequencies determine the radar’s resolution, range, and application. The concept of radar bands dates back to World War II, where letters were used for confidentiality. These letter designations stuck and are still widely used today.
Most radar systems operate between 30 MHz and 300 GHz, corresponding to wavelengths from 10 meters down to 1 millimeter.
🔍 Common Radar Bands
Here’s a breakdown of the most commonly used radar bands:
| Band | Frequency Range | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| P Band | 230–1000 MHz | Over-the-horizon radar, foliage penetration |
| L Band | 1–2 GHz | Air traffic control, weather radar |
| S Band | 2–4 GHz | Surface ship radar, long-range weather radar |
| C Band | 4–8 GHz | Weather radar, satellite communications |
| X Band | 8–12.5 GHz | Military tracking, missile guidance, marine |
| Ku Band | 12.5–18 GHz | Satellite communications, police radar |
| K Band | 18–26.5 GHz | Short-range applications, altimeters |
| Ka Band | 26.5–40 GHz | High-resolution satellite radar, 5G systems |
🌐 Expanding Into Higher Frequencies
As technology evolves, radar systems are pushing into higher frequency ranges, including terahertz bands. These ultra-high-frequency ranges allow for even finer resolution and compact radar systems, playing a vital role in next-gen applications like autonomous driving and advanced imaging.
🔬 Other Microwave Bands Worth Knowing
Beyond the commonly used radar bands, the microwave frequency spectrum includes a wide array of designated bands for various RF and mmWave uses:
| Band | Frequency Range | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Q Band | 30–50 GHz | Automotive radar, imaging |
| U Band | 40–60 GHz | Communication satellites |
| V Band | 50–75 GHz | Wireless gigabit networks |
| E Band | 60–90 GHz | High-capacity backhaul links |
| W Band | 75–110 GHz | Millimeter-wave radar systems |
| F Band | 90–140 GHz | Terahertz experiments, sensing |
| D Band | 110–170 GHz | Ultra-high resolution radar |
🚀 Final Thoughts
Understanding radar frequency bands is essential for RF engineers, system designers, and tech professionals working in advanced communication and sensing systems. Whether you’re integrating radar into aerospace platforms or building automotive driver-assist systems, choosing the right frequency band affects everything—from performance to regulatory compliance.
As demand for higher resolution and faster data increases, radar technology continues to evolve—pushing into terahertz territory and beyond.
🌟 Discover Precision RF Components from Reach-line
Need precision components for your radar systems? Reach-line offers a wide range of RF connectors, cable assemblies, and adapters designed for high-frequency applications, including X, Ku, K, Ka, and W bands.
🔗 Explore Reach-line’s product line to power your next radar innovation with reliability and performance.
STAY IN FOR MORE NEWS
Subscribe to our free newsletter.
RF, microwave, and millimeter-wave describe frequency ranges with distinct uses. RF covers 3 kHz to 300 GHz, including microwaves and mmWave. Microwaves occupy 300 MHz to 300 GHz, while mmWave strictly focuses on 30 GHz to 300 GHz. Each handles specific tech needs.
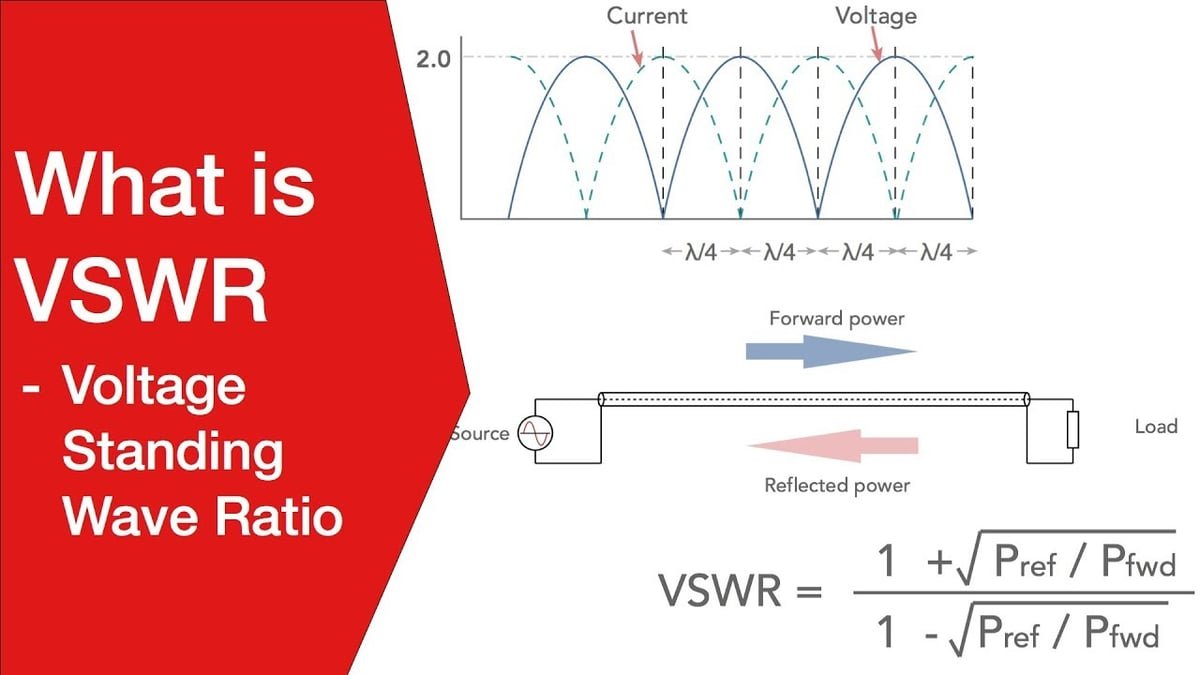
Introduction to VSWR Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) is a critical parameter in RF (Radio Frequency) systems, indicating how effectively power is transferred from a source to a load. It measures the ratio of the maximum to the minimum voltage in a standing wave formed by reflected and transmitted signals.
The evolution of 5G technology has brought immense benefits—but also unprecedented challenges—particularly in the field of RF testing and measurement. As new technologies like millimeter wave, beamforming, and ultra-wideband become essential to 5G, traditional testing methods are no longer sufficient. Over-the-air (OTA) testing is now central to ensuring performance and compliance with 5G NR standards.
Discover Reach-Line’s precision RF and microwave terminations covering DC to 110 GHz and power levels 1 W to 1000 W. Reliable, low VSWR solutions for 5G, satellite, and lab applications.